Dental implants are commonly recommended for adults, but a child also needs an implant for the absence of teeth, which may be caused by genetic factors or trauma. Implants help restore a child’s self-confidence and their feeling of being socially accepted. However, dental implants in children should have special considerations. In this post, you’ll learn the signs to look out for if your child needs a dental implant. 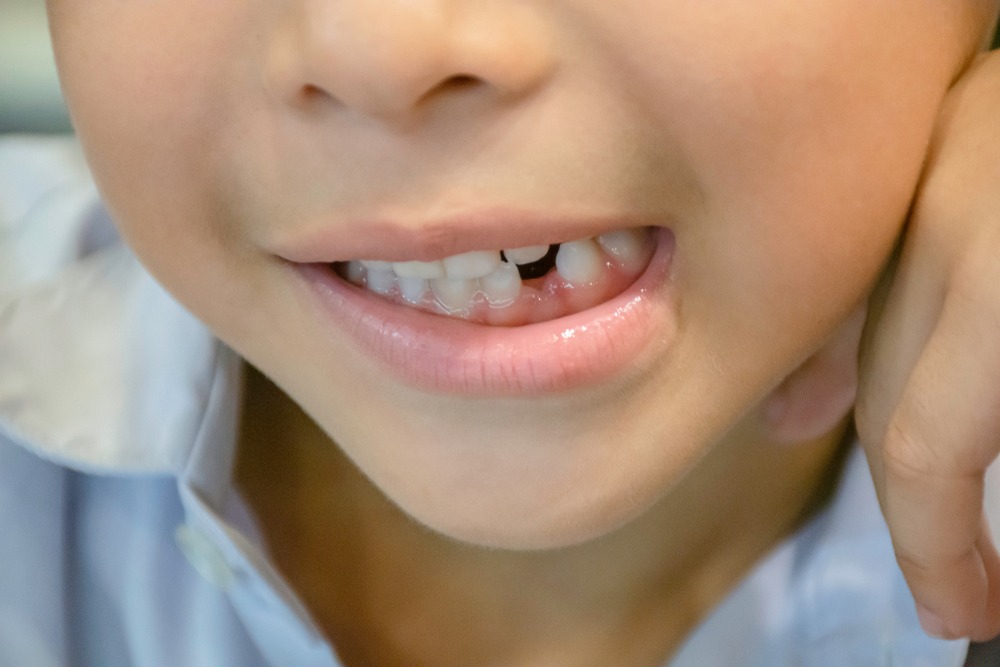 Noticeable Absence or Loss of Teeth Since Birth Anodontia or congenital absence of teeth can be caused by trauma or can be congenitally acquired. A pediatric dentist should be sought if you notice that your child does not have teeth since birth.Here are quick facts about anodontia:
Noticeable Absence or Loss of Teeth Since Birth Anodontia or congenital absence of teeth can be caused by trauma or can be congenitally acquired. A pediatric dentist should be sought if you notice that your child does not have teeth since birth.Here are quick facts about anodontia:
- Complete anodontia is a rare condition that refers to the congenital absence of your child’s teeth in the permanent or primary dentition (all teeth involved).
- Oligodontia or hypodontia is the absence of a tooth or a few teeth, which manifests in many genetic conditions. The third molars are the most frequently missing teeth but not requiring prosthetic replacement. Missing mandibular second premolars, maxillary second premolars, maxillary lateral incisors, and mandibular incisors are usually the ones needing dental replacement or dental implant. Visit a Syracuse family dentist for more information about dental implants.
Teeth Protrusion Teeth proclination refers to the protrusion of teeth, usually affecting the upper and lower incisors. The lips tend to become incompetent and protruding. These conditions are predisposing factors for front tooth trauma that commonly result in avulsion or injury of maxillary incisors. Here are the stats in one Australian study concerning the incidence of tooth trauma among children:
- The incidence of front tooth trauma in children ages 6 to 12 years old is 1.7 patients per 100 children per year.
- The prevalence of trauma reported worldwide ranges from 11% to 30%, which is very concerning among parents and children involved.
Lack of Confidence Due to Multiple Missing Teeth Loss of teeth may lead to loss of function. It results in unpleasant aesthetics, hampering the psychosocial development of a young child. If you believe that your child has anodontia, talking to a pediatric dentist is a must, most especially if you notice behavioral changes, as well as the deterioration of social relationships and the academic performance of your child. The management of a single tooth loss in children is done using conservative methods. If there are large pulp chambers in immature teeth, the pulp loses its vitality, which warrants complete coverage restorations, that’s why dentists resort to partial coverage prosthesis or dental implants of multiple missing teeth. Here’s how dentists implement dental implants for children using a multidisciplinary approach:
- As soon as anodontia is diagnosed, the pediatric dentist will ask you to let your child be seen by the dentist at a very young age. Your child remains under the same pediatric dentist’s care for an extended period to help prepare your child, and allow sufficient time to create appropriate treatment planning.
- The dentist will take into consideration important factors when treating your child with a missing tooth, including their health condition, growth, presence of dentition, amount of alveolar bone, residual space between teeth, and the right timing of dental implants.
- For later dental implants or implant placements, it’s essential to preserve the primary teeth until the root is restored, as well as prevent dental caries and bone loss. The pediatric dentist will help you manage your child’s oral care to better prepare them for a dental implant.
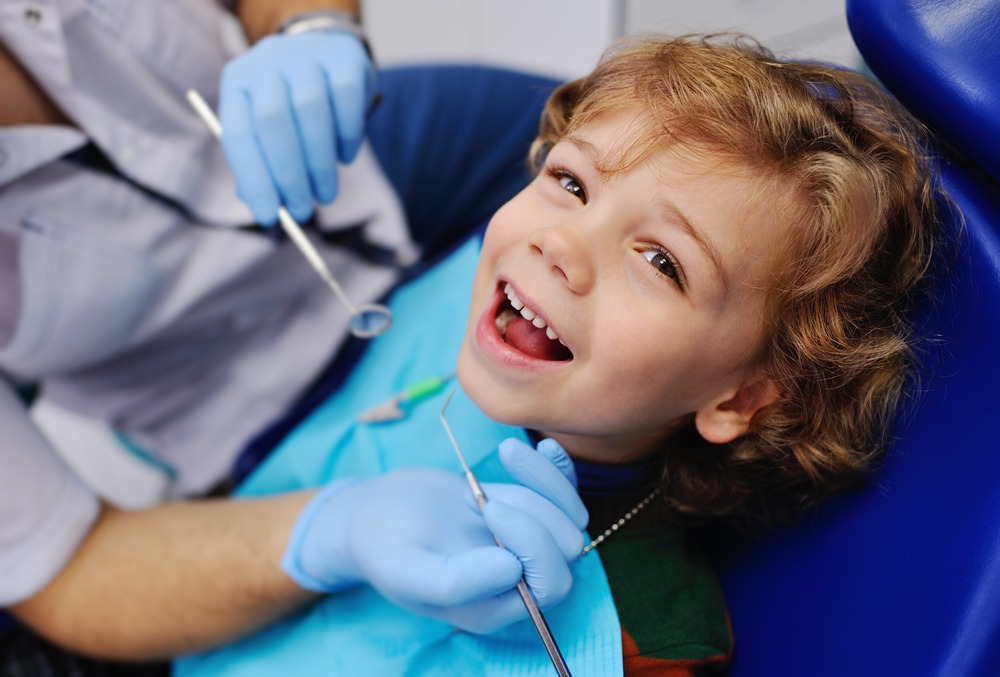
Unpleasant Tooth Appearance Protrusion of multiple teeth needs appropriate orthodontic intervention to make the appearance of the teeth aesthetically pleasing. A dental implant is an orthodontic treatment to consider. Here’s how a dental implant is done:
- The orthodontist will create appropriate spaces for dental implant insertion.
- The orthodontist will correct the root angulations of your child’s permanent teeth in the jaw bone. Proper root alignment will help reduce angular defects, which may lead to bone loss.
- Bone assessment is usually carried out through a CT-scan or computed tomography scan.
- Stabilization of the teeth occlusions and arches are all carried out before the dental implant.
- Also, bone grafting might be required to improve hard tissue topography for a harmonious crestal ridge contour (crestal bone holds the teeth in place).
- Orthodontic retainers will be given to a child during the primary bone healing phase of the dental implant.
ConclusionTrauma, severely malposed teeth, and congenitally missing teeth require bone augmentation procedures. In dental implant surgery, it entails the collaboration of a multidisciplinary team, including a pediatric dentist, prosthodontist, an orthodontist, and maxillofacial surgeon. This is done to ensure the successful outcome of dental implants in children.
I’m a 20-something stay-at-home mother and wife. I have an amazing husband, a beautiful daughter, two loving dogs, and a lazy cat. I wouldn’t change my life for anything! I love to read, listen to music, cook and blog!

Speak Your Mind